Page 32 - ingilizce
P. 32
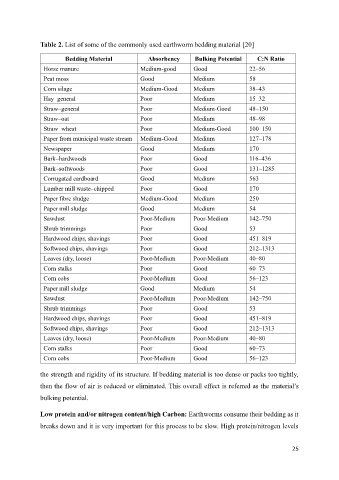
Table 2. List of some of the commonly used earthworm bedding material [20]
Bedding Material Absorbency Bulking Potential C:N Ratio
Horse manure Medium-good Good 22–56
Peat moss Good Medium 58
Corn silage Medium-Good Medium 38–43
Hay–general Poor Medium 15–32
Straw–general Poor Medium-Good 48–150
Straw–oat Poor Medium 48–98
Straw–wheat Poor Medium-Good 100–150
Paper from municipal waste stream Medium-Good Medium 127–178
Newspaper Good Medium 170
Bark–hardwoods Poor Good 116–436
Bark–softwoods Poor Good 131–1285
Corrugated cardboard Good Medium 563
Lumber mill waste–chipped Poor Good 170
Paper fibre sludge Medium-Good Medium 250
Paper mill sludge Good Medium 54
Sawdust Poor-Medium Poor-Medium 142–750
Shrub trimmings Poor Good 53
Hardwood chips, shavings Poor Good 451–819
Softwood chips, shavings Poor Good 212–1313
Leaves (dry, loose) Poor-Medium Poor-Medium 40–80
Corn stalks Poor Good 60–73
Corn cobs Poor-Medium Good 56–123
Paper mill sludge Good Medium 54
Sawdust Poor-Medium Poor-Medium 142–750
Shrub trimmings Poor Good 53
Hardwood chips, shavings Poor Good 451–819
Softwood chips, shavings Poor Good 212–1313
Leaves (dry, loose) Poor-Medium Poor-Medium 40–80
Corn stalks Poor Good 60–73
Corn cobs Poor-Medium Good 56–123
the strength and rigidity of its structure. If bedding material is too dense or packs too tightly,
then the flow of air is reduced or eliminated. This overall effect is referred as the material’s
bulking potential.
Low protein and/or nitrogen content/high Carbon: Earthworms consume their bedding as it
breaks down and it is very important for this process to be slow. High protein/nitrogen levels
25